Prospective studies, including randomized controlled trials, are much more reliable forms of evidence. And in recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of prospective studies on artificial neural networks. This shift towards more reliable research methods has convinced many clinicians that ANNs are worth using in healthcare today.
Paul Cerrato, a senior research analyst and communication specialist at Mayo Clinic Platform, is a strong advocate for the use of artificial neural networks in healthcare. With a background in data mining and machine learning, Cerrato has been widely published in peer-reviewed medical literature and has authored several books on digital health. His expertise in this field has led him to be named one of the most influential bloggers by HIMSS and to be inducted into Sigma Xi, the Scientific Research Honor Society.
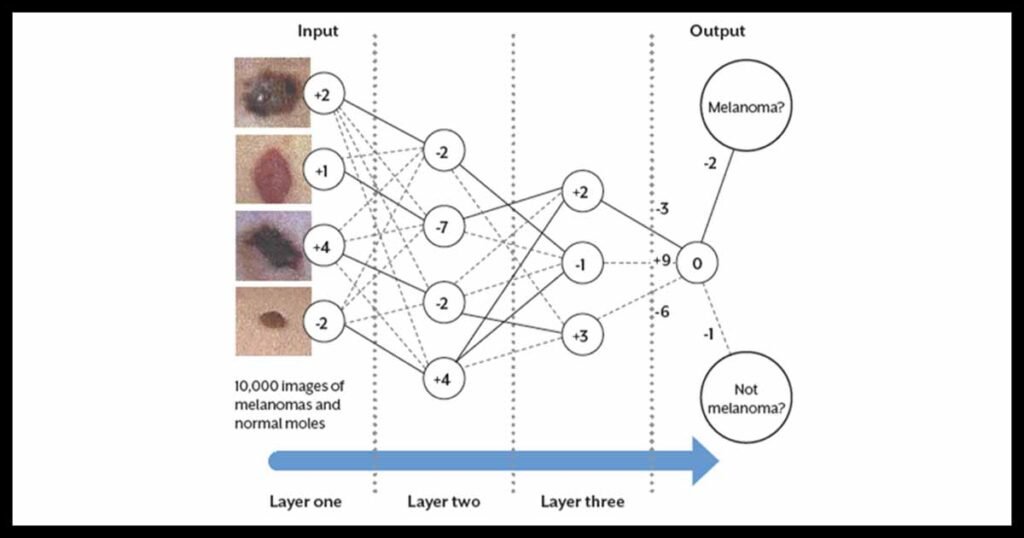
In a recent interview with Healthcare IT News, Cerrato provided a deep dive into artificial neural networks, explaining how they work and why they are gaining traction in healthcare. He described ANNs as a collection of interconnected nodes, similar to the neurons in the brain. These networks are trained on large datasets, such as images of skin lesions, to analyze data and generate results.
The training process involves feeding the network with labeled data, known as ground truth, to help it learn the correct answers. The network then goes through a testing phase where it must generate answers without knowing the correct outcome. The accuracy of the network during testing determines its effectiveness in making diagnoses or predictions.
What sets ANNs apart is their ability to learn and adapt from data, making them valuable tools in healthcare. With the increasing number of prospective studies supporting their use, many clinicians are starting to recognize the potential of artificial neural networks in improving patient care.
In conclusion, artificial neural networks have come a long way since their inception in the 1950s. With advancements in technology and research methods, these networks are becoming more reliable and effective in healthcare. As clinicians continue to explore the possibilities of ANNs, we can expect to see even greater advancements in the field of digital health. Artificial neural networks have been gaining traction in the medical field, with many doctors and thought leaders starting to believe in the power of these tools. Mayo Clinic, for example, has implemented several programs utilizing ANNs, with impressive results.
One such program at Mayo Clinic focuses on improving the accuracy of colonoscopies by using ANNs. These networks have significantly increased the adenoma detection rate, which measures the ability to detect precancerous polyps in the colon. This improvement has led to more lives being saved and has convinced many doctors of the effectiveness of ANNs.
The Eagle Study conducted at Mayo Clinic is another example of the success of ANNs in healthcare. This randomized controlled study utilized an artificial neural network in combination with an EKG to detect a weak heart pump, a risk factor for heart failure. Clinicians using the AI showed better results in identifying patients at risk, further solidifying the belief in the efficacy of ANNs.
Large language models (LLMs) are another specialized type of ANN that has been making waves in the medical field. These models draw on massive data sets to generate algorithms that can diagnose diseases, summarize patient records, and even answer patient emails. When carefully constructed and validated, LLMs can provide concise summaries of electronic health records, helping doctors make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
While ANNs and LLMs have shown great promise in diagnosis and record summarization, they also have the potential to assist in patient communication. Doctors can rely on AI to answer simple patient queries, such as side effects of a prescribed medication or the need for a follow-up appointment. This not only saves time for doctors but also ensures that patients receive accurate and timely information.
Although the implementation of ANNs and LLMs in healthcare is still a work in progress, the success stories from Mayo Clinic and other institutions are encouraging. These tools have the potential to revolutionize the way medical professionals diagnose and treat patients, ultimately leading to better outcomes and improved patient care.
In conclusion, the growing body of evidence supporting the use of artificial neural networks in healthcare is convincing more doctors and thought leaders of their value. With continued research and development, ANNs and LLMs have the potential to transform the medical field and improve patient outcomes.