In a world where technology is constantly evolving, the field of medicine is no exception. Recent advancements have paved the way for personalized healthcare solutions that take into account individual differences in genetics, environment, and lifestyle. One such groundbreaking development is the creation of a personalized “digital twin” by researchers from Prof. Eran Segal’s laboratory at the Weizmann Institute of Science.
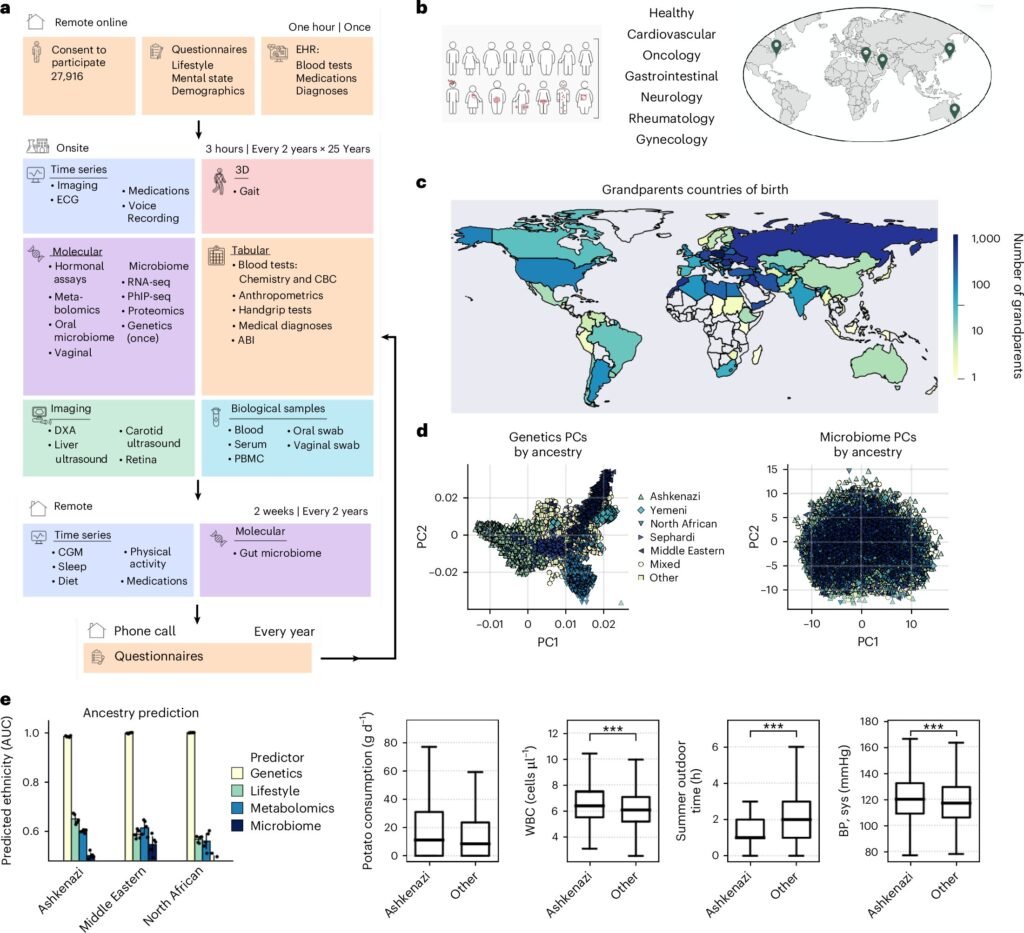
This innovative approach harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to analyze extensive medical data collected from over 13,000 individuals as part of the Human Phenotype Project. This project, initiated in 2018, aims to create a comprehensive database of human health information by tracking participants through extensive medical assessments and testing every two years over a 25-year period.
The data collected includes measurements from 17 different body systems, nutritional logs, gene sequencing, cellular protein analysis, and microbiome analysis, among others. By combining this wealth of information with AI algorithms, researchers are able to create a personalized digital twin for each participant. This digital twin allows for the prediction of future health outcomes, the detection of disease risks, and the identification of personalized treatment options.
One of the key aspects of this research is the study of biological age, which offers insights into the aging process and potential health risks. By analyzing physiological changes in different body systems and comparing them to expected patterns, the AI model developed by Drs. Lee Reicher and Smadar Shilo can determine a participant’s biological age. This information can help identify individuals at risk of developing diseases such as diabetes, breast cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The digital twin model is also capable of predicting future health events and recommending preventive measures or treatment options. By analyzing glucose levels, for example, the model can predict the likelihood of developing diabetes and suggest dietary changes or medications to prevent the disease. This personalized approach to healthcare has the potential to revolutionize the field by providing tailored treatment plans based on individual characteristics and health trajectories.
As the research team continues to refine the digital twin model and expand the Human Phenotype Project to include more participants and diverse populations, the possibilities for personalized medicine are endless. By leveraging AI technology and extensive health data, researchers are paving the way for a future where healthcare is truly personalized, preventive, and precise.
This groundbreaking research, detailed in a recent publication in Nature Medicine, highlights the transformative potential of AI-driven healthcare and underscores the importance of collaboration between researchers, participants, and the scientific community. With the support of dedicated individuals and innovative technology, the future of medicine looks brighter than ever before.