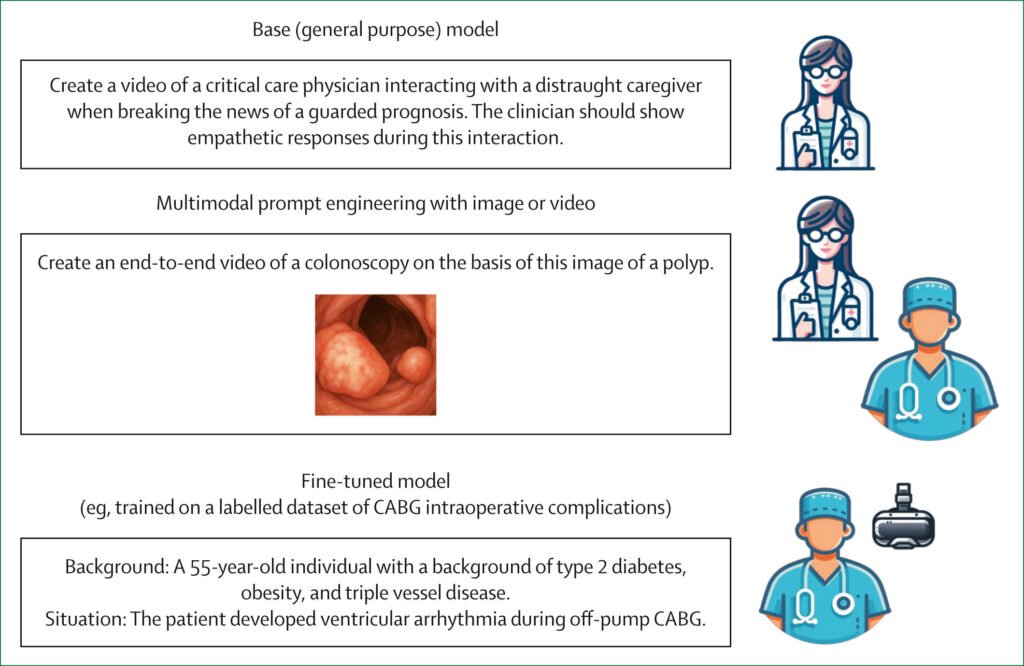
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of medical education, offering innovative ways to train doctors and healthcare professionals more efficiently and effectively. A recent study published in The Lancet Digital Health highlights the transformative potential of AI in medical education, emphasizing the need for collaboration across various stakeholders to ensure its safe and responsible implementation.
As the global healthcare system grapples with a looming shortage of healthcare workers, estimated to reach 10 million by 2030, AI presents a promising solution to bridge the gap. By leveraging technologies such as large language models (LLMs) and virtual reality, AI can personalize learning experiences, simulate realistic clinical scenarios, and streamline tasks like literature reviews. These advancements not only enhance the quality of medical education but also enable healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills and improve patient care outcomes.
However, the widespread adoption of AI in medical education faces challenges such as a lack of qualified trainers, ethical considerations, and concerns about biases and privacy. To address these issues, the study advocates for a collaborative approach involving medical schools, healthcare institutions, industry partners, and regulators. By working together, these stakeholders can develop responsible and scalable AI-enabled training programs that prioritize patient safety, learning integrity, and ethical use of AI tools.
Dr. Jasmine Ong, a Principal Clinical Pharmacist at Singapore General Hospital and a joint first author of the study, emphasizes that AI is meant to empower educators and mentors, not replace them. By serving as a digital co-tutor, AI enhances the learning experience by providing personalized feedback and realistic simulations, ultimately shaping the next generation of healthcare professionals.
Dr. Ning Yilin, a Senior Research Fellow at Duke-NUS’ Center for Quantitative Medicine and joint first author of the paper, underscores the importance of addressing ethical concerns and designing inclusive, responsible AI solutions. As AI becomes more integrated into medical education and training, clear guidance and ethical frameworks are essential to prevent unintended harms and biases.
Associate Professor Liu Nan, the director of the Duke-NUS AI + Medical Sciences Initiative and a senior author of the study, advocates for a comprehensive global strategy to promote the responsible adoption of AI in medical education. By fostering cross-sector partnerships and developing evidence-based solutions, stakeholders can harness the full potential of AI to enhance training programs and improve patient care outcomes.
In conclusion, collaboration is key to unlocking the transformative potential of AI in medical education. By working together, stakeholders can overcome challenges, establish best practices, and create a more interactive and accessible training environment for healthcare professionals. Through sustained partnerships and innovative initiatives, the integration of AI in medical education holds the promise of revolutionizing the way doctors are trained and ultimately improving healthcare delivery for patients worldwide.