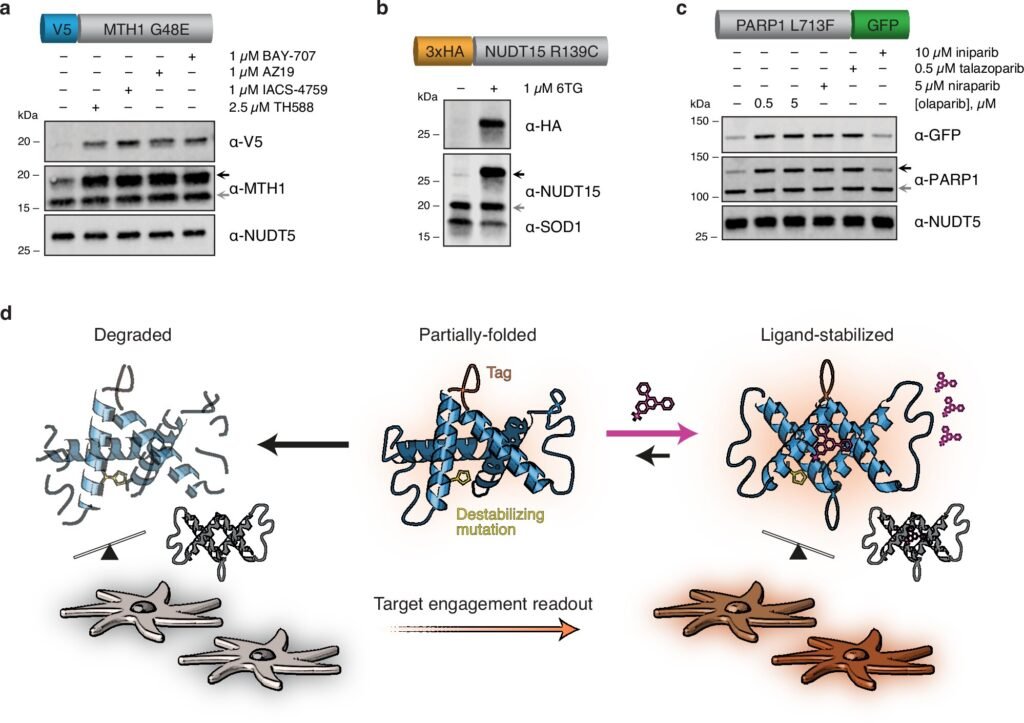
A groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications has unveiled a new method in drug discovery and development known as CeTEAM. Developed by researchers at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, this innovative approach aims to bridge the gap between how drugs bind to their targets within cells and the resulting effects they produce. By offering a deeper insight into the mechanisms of drug action, CeTEAM has the potential to revolutionize the way new therapies are developed and evaluated, ultimately leading to improved treatments for patients.
Nicholas Valerie, Assistant Professor at the Department of Laboratory Medicine and the lead author of the study, explains the significance of CeTEAM in understanding drug interactions within live cells. He highlights how this method can shed light on the intended effects as well as any unintended side effects of drugs, using variants of known therapeutic targets like the DNA repair protein PARP1 as examples. By visualizing drug interactions at a cellular level, researchers can gain valuable insights into how drugs impact cellular function and therapeutic responses.
One of the key advantages of CeTEAM is its ability to measure drug-protein interactions without altering the cellular environment. This allows researchers to monitor the effects of drugs over time and unravel their mechanism of action. Mikael Altun, Associate Professor at the Department of Laboratory Medicine and a senior author of the study, emphasizes the efficiency of CeTEAM in screening multiple drugs simultaneously, making the drug discovery process faster and more effective. Additionally, this method provides a valuable tool for studying drug interactions in preclinical models, offering a comprehensive understanding of drug mechanisms in complex biological systems.
Looking ahead, the research team is optimistic about the potential applications of the CeTEAM method. Future endeavors include exploring the effectiveness of different protein variants in the method, expanding its use across various drug types, and investigating drug target selectivity in cells. Valerie underscores the impact of this method on accelerating the discovery of new drugs for diverse diseases, emphasizing its potential to benefit patients worldwide.
For more information on the study, readers can refer to the publication in Nature Communications titled “Coupling cellular drug-target engagement to downstream pharmacology with CeTEAM” by Nicholas C. K. Valerie et al. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54415-7). The Karolinska Institutet has provided this groundbreaking research, paving the way for advancements in drug discovery and development.
This article is based on the original content published on Medical Xpress, retrieved on December 6, 2024, and is subject to copyright. Reproduction of any part of this content without written permission is prohibited. The information provided is for educational and informational purposes only.