Digital health care is a rapidly growing field that relies on technology to provide remote medical services, monitor patient health, and improve overall wellness. While tools such as telehealth, mobile health apps, and wearable devices have the potential to revolutionize the way health care is delivered, a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Queensland highlights the importance of trust in these digital health solutions.
Dr. Soraia de Camargo Catapan and Dr. Jaimon Kelly from UQ’s Center for Online Health conducted a comprehensive review of 49 studies spanning over 13 years to identify the factors influencing trust in digital health care among consumers and health care professionals. The findings of their research were published in the journal npj Digital Medicine.
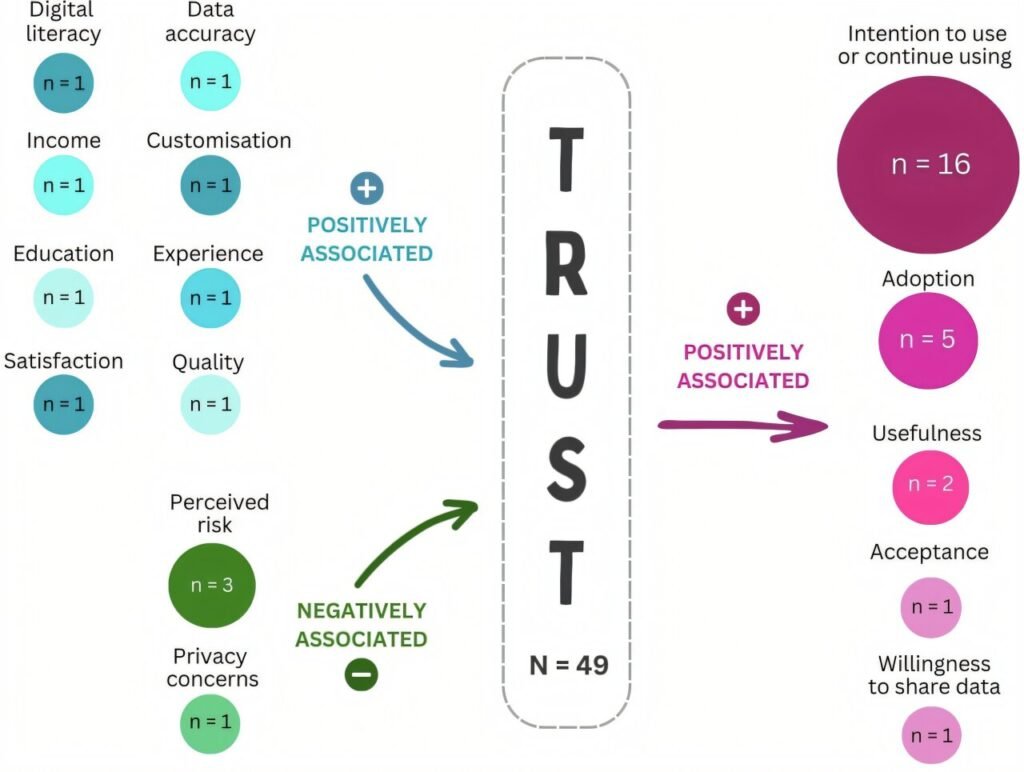
According to Dr. Catapan, trust is a crucial element in the adoption of digital health care technologies. Without trust, individuals may be hesitant to use these tools, leading to lower engagement and potentially hindering the effectiveness of digital health interventions. Factors influencing trust include digital literacy, education levels, prior experiences with digital health, income, privacy concerns, and perceived risks associated with using digital health technologies.
The quality of digital health care, data accuracy, and the level of human interaction in automated interventions also play a significant role in building trust among users. Dr. Kelly emphasized that trust directly impacts consumer behavior and can influence the adoption and utilization of digital health technologies.
The study also highlighted the importance of considering cultural and geographical differences when assessing trust in digital health care. For example, in China, where digital privacy is more regulated, perceptions of trust may differ significantly from those in Western countries. Understanding these differences is essential for the successful implementation of digital health solutions on a global scale.
The researchers believe that building trust in digital health care is essential for improving health outcomes, increasing the adoption of digital health technologies, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of these solutions. By developing a comprehensive framework for trust in digital health care, stakeholders can create a more supportive environment for the use of digital health tools and ultimately enhance the delivery of care.
Overall, the study sheds light on the critical role of trust in digital health care and underscores the need for further research and initiatives to promote trust among consumers and health care professionals. As the field of digital health continues to evolve, building trust will be key to maximizing the potential benefits of these innovative technologies.