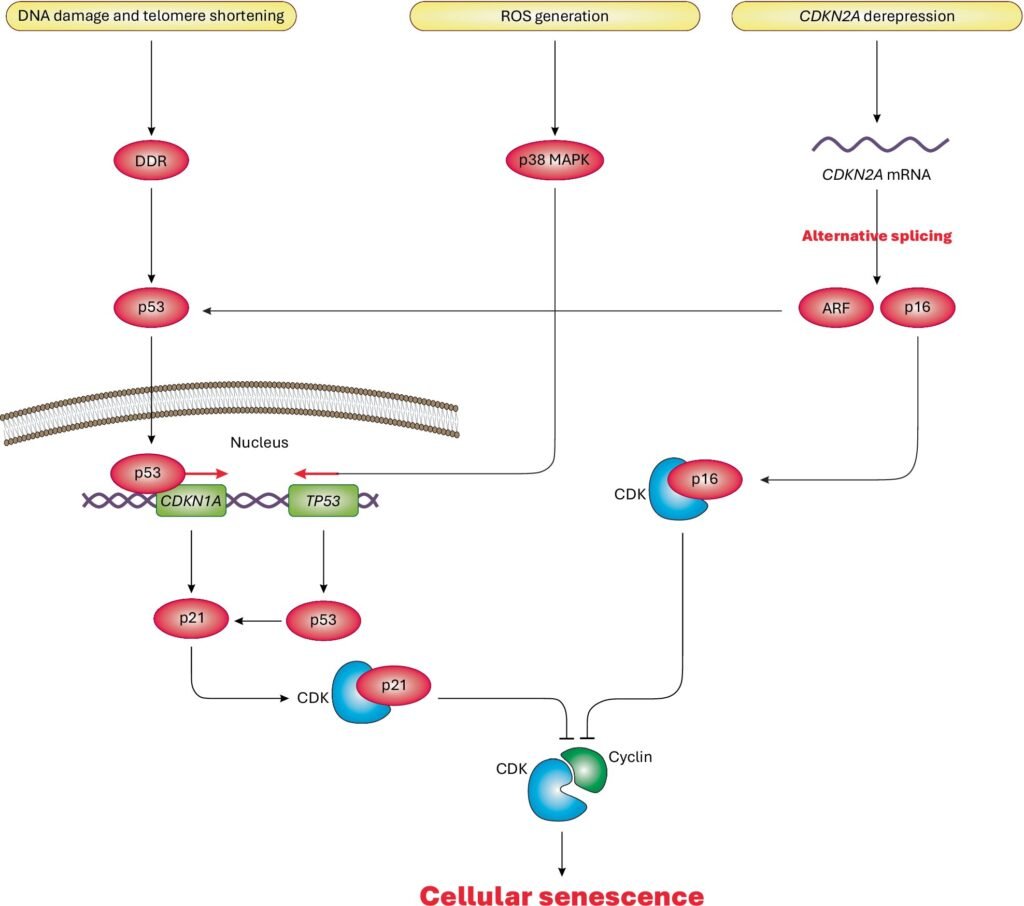
Cellular senescence is a crucial process where the cell cycle is permanently arrested, preventing cell division, proliferation, and growth. This phenomenon can be triggered by various cellular stresses, including DNA damage, telomere shortening, and oxidative stress. While cellular senescence plays a vital role in tissue development, repair, and biological processes like embryogenesis, it also contributes to age-related diseases, certain cancers, Alzheimer’s disease, and other conditions.
A recent paper titled “Hallmarks of cellular senescence: biology, mechanisms, regulations,” published in Experimental & Molecular Medicine, delves into the latest research findings on cellular senescence in experimental and human disease models. The study focuses on the molecular mechanisms, regulation, and future research directions to advance the field and facilitate therapeutic translation.
The authors of the paper highlight that cellular senescence acts as a protective measure for cells under extreme stress conditions such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, and telomere shortening. The impacts of senescent cells, both physiological and pathological, are largely governed by unknown mechanisms, limiting the translational relevance of current findings. As a result, further studies are necessary to address unanswered questions and bridge existing gaps.
The researchers provide valuable insights into new research avenues and potential challenges for therapeutic interventions targeting cellular senescence in related conditions. By conducting additional experimental studies, they aim to comprehensively understand and address all aspects of this process.
One of the co-authors of the paper is Domenico Praticò, MD, the Scott Richards North Star Foundation Chair for Alzheimer’s Research and a Professor of Neural Sciences at the Alzheimer’s Center at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM).
For more information, you can refer to the paper titled “Hallmarks of cellular senescence: biology, mechanisms, regulations” published in Experimental & Molecular Medicine in 2025 with DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01480-7.
This information was provided by the Alzheimer’s Center at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine.
Citation:
Cellular senescence may be to blame for some diseases (2025, July 22) retrieved 23 July 2025 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-07-cellular-senescence-blame-diseases.html
Please note that this document is subject to copyright, and any reproduction without written permission is prohibited. The content is intended for informational purposes only.