Embryonic macrophages have been identified as key players in the regulation of blood stem cell numbers in the bone marrow, shedding light on their crucial role in the lifelong production of blood cells and immune system function. A recent study conducted at the Leibniz Institute on Aging—Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) in Jena has uncovered a previously unknown function of these specialized phagocytes of the immune system.
Hematopoietic stem cells are responsible for replenishing the immune and blood cell populations, which have a limited lifespan and need to be constantly renewed. The process of blood cell formation occurs in the bone marrow, within a specialized microenvironment known as the hematopoietic niche. This niche is crucial for supporting the continuous production of blood cells and maintaining a healthy immune system, yet the mechanisms underlying its formation during development have remained elusive.
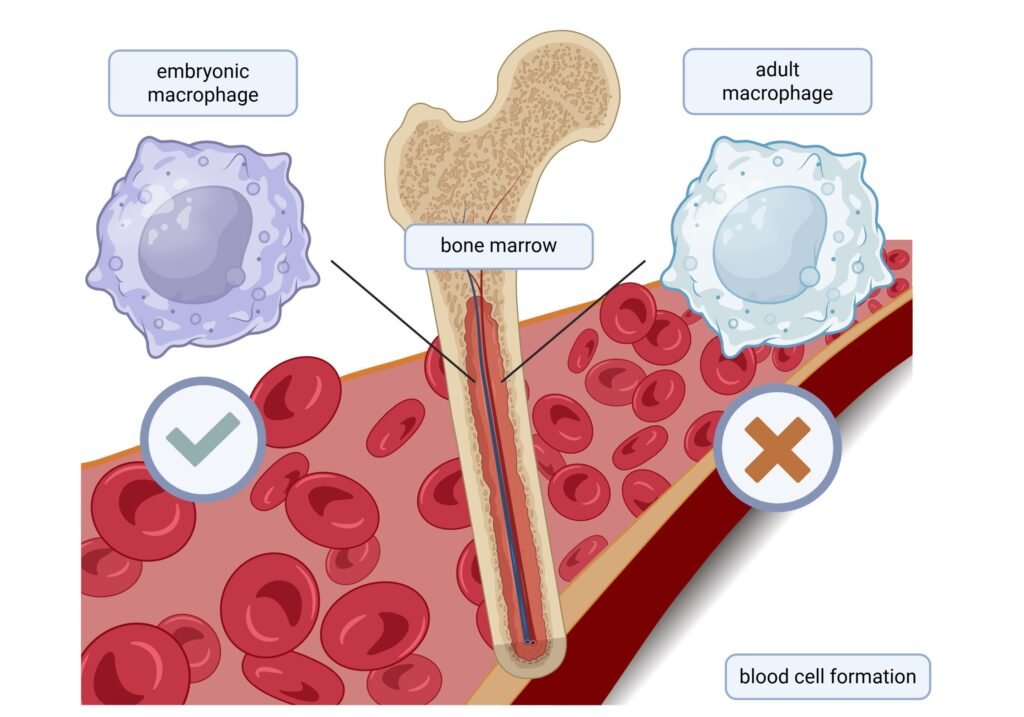
The research team led by Prof. Claudia Waskow at FLI has revealed that embryonic macrophages play a critical role in the regulation of blood stem cells within the bone marrow. These macrophages, which are present before birth, orchestrate the set-up of the stem cell niche, influencing the size of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. This discovery, published in Nature Communications, highlights the importance of embryonic macrophages in shaping the bone marrow microenvironment.
The study identified two distinct populations of macrophages in the bone marrow—one with an embryonic origin and another derived from hematopoietic stem cells after birth. While these macrophages share similar external characteristics, they differ significantly in their functions. Embryonic macrophages are specifically responsible for regulating the number of blood stem cells in the bone marrow, impacting the production of progenitor cells essential for blood cell formation throughout life.
The absence of embryonic macrophages disrupts the migration of hematopoietic stem cells into the bone marrow, affecting their ability to populate the stem cell niche. These specialized cells secrete signals that guide stem cells to their destination within the bone marrow, a process crucial for the continuous production of blood cells and immune defense.
By unraveling the role of embryonic macrophages in hematopoiesis, this study provides new insights into the complex interactions that shape the bone marrow microenvironment. Understanding the regulatory mechanisms underlying the establishment and maintenance of adult hematopoiesis could pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches to promote healthy aging and combat age-related diseases.
Overall, this research underscores the multifaceted functions of bone marrow macrophages and emphasizes their active role in controlling hematopoietic activity. By delving into the ontogenesis of macrophages and their impact on blood stem cell regulation, scientists aim to advance our knowledge of immune system function and develop targeted interventions for promoting healthy aging.