Stem cells are a vital component of the body’s regenerative processes, with the potential to differentiate into various cell types to aid in tissue repair and growth. However, one of the challenges they face is immune rejection when transplanted into a new environment. Researchers have now uncovered a crucial mechanism that allows stem cells to evade immune detection, creating immune-privileged sites where they can thrive without being attacked by the immune system.
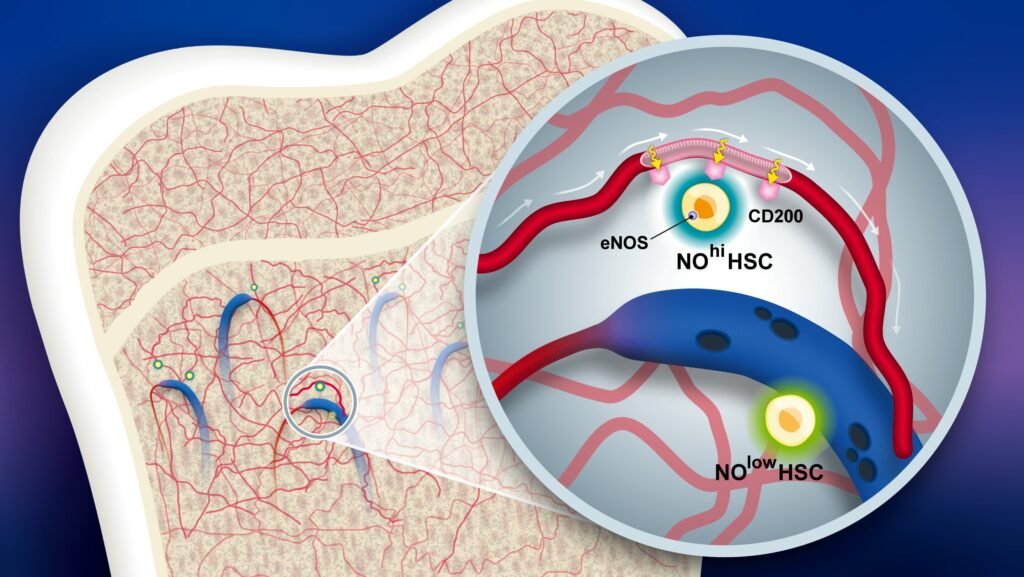
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature, a team of international scientists led by Kazuhiro Furuhashi and Joji Fujisaki delved into the world of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) responsible for generating blood cells. These specialized stem cells produce nitric oxide (NO) as a means to manipulate the immune response and ensure their safe reproduction. The researchers identified a subset of HSCs known as NOhi HSCs, which express high levels of NO and the immunomodulatory receptor CD200R—a key player in immune suppression and tolerance.
Furthermore, the survival of NOhi HSCs was found to be dependent on their proximity to specialized blood vessels with a unique hairpin-curve shape. These vessels create increased shear stress, which in turn regulates stem cell behavior by elevating NO levels. This optimal microenvironment enables NOhi HSCs to proliferate and evade immune detection, shedding light on the critical role of blood vessels in maintaining stem cell function and immune balance.
The discovery not only enhances our understanding of stem cell survival mechanisms but also redefines the role of blood vessels as gatekeepers that regulate stem cell activity and immune responses. This breakthrough could revolutionize regenerative medicine and immunotherapy, offering new insights into the development of immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory treatments. Additionally, these findings may have implications for cancer treatment, as similar immune regulatory mechanisms involving CD200 have been identified in tumor-associated blood vessels.
Moving forward, this research opens doors for novel therapeutic approaches and highlights the intricate interplay between stem cells, blood vessels, and immune responses. By unraveling the complex mechanisms that govern stem cell survival and immune evasion, scientists are paving the way for transformative advancements in healthcare and disease treatment.
Reference:
Kazuhiro Furuhashi et al, Bone marrow niches orchestrate stem-cell hierarchy and immune tolerance, Nature (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08352-6.