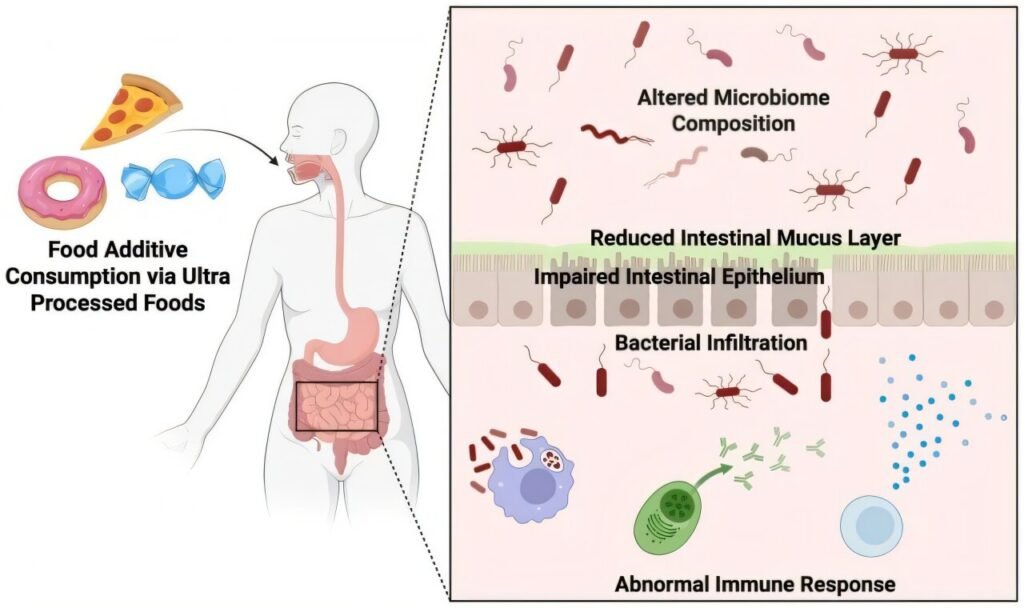
Food additives are commonly used in ultra-processed foods to enhance their shelf life, appearance, and taste. However, recent studies have shown that these additives can have negative effects on gut health. Researchers have found that exposure to certain food additives, such as artificial colorants, sweeteners, emulsifiers, and preservatives, can disrupt the gut microbiome, reduce the intestinal mucus layer, impair barrier function, and trigger abnormal immune responses.
Animal studies have provided valuable insights into the potential harmful effects of food additives on the gastrointestinal tract. For example, artificial colorants and sweeteners have been shown to exacerbate intestinal inflammation, alter intestinal permeability, and disrupt the gut microbiome in animal models. These findings suggest that food additives may play a role in the development of gastrointestinal disorders in humans.
While most of the existing research on food additives has been conducted in animal models, there is a growing need for more clinical studies to assess the impact of these compounds on human gut health. In the meantime, researchers recommend policy changes to help consumers make more informed choices. For example, food manufacturers could be required to list the amount of each food additive on product labels, allowing consumers to track their consumption more effectively. Additionally, warning labels could be included on products containing potentially harmful additives, similar to regulations in the European Union.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Food Safety Authority are already re-evaluating the safety of food additives, indicating a growing recognition of the potential risks associated with these compounds. By increasing awareness of the potential harmful effects of food additives on gut health and implementing policy changes to regulate their use, we can take steps towards protecting the gastrointestinal health of consumers. More research is needed to fully understand the impact of food additives on human health, but in the meantime, consumers can make more informed choices by opting for additive-free foods whenever possible.