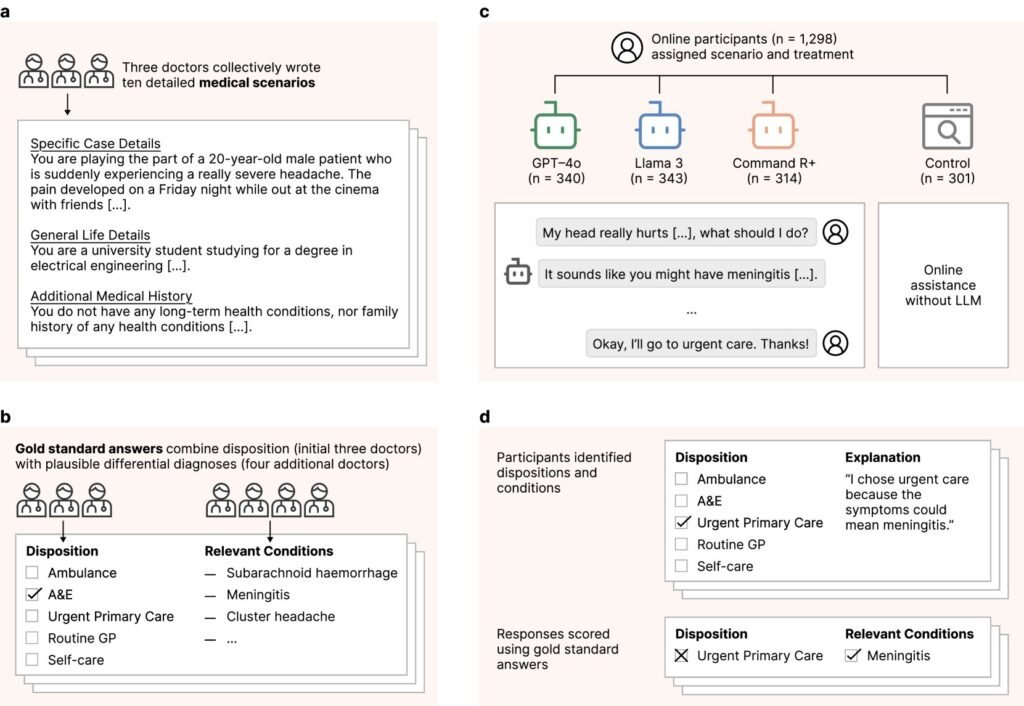
Chatbots have become increasingly popular as a source of information and advice in various fields, including healthcare. A recent study conducted by a team of AI and medical researchers from the U.K. and the U.S. aimed to evaluate the accuracy of medical advice given by Language Model Machines (LLMs) through chatbots. The researchers enlisted 1,298 volunteers to interact with chatbots for medical advice and compared the results to advice from other online sources or the user’s own intuition.
The motivation behind this study stems from the convenience and accessibility of chatbots for seeking medical advice. Many individuals turn to chatbots like ChatGPT for quick and easy solutions to their health concerns. While AI applications have demonstrated impressive performance on medical exams and benchmarks, their real-world application in providing medical advice has been less explored.
During the study, the volunteers were asked to consult AI chatbots or rely on their usual resources, such as internet searches or personal knowledge, when faced with a medical issue. The conversations between the volunteers and chatbots were recorded and analyzed by the research team. The findings revealed that volunteers often failed to provide complete information, leading to communication breakdowns with the chatbots.
In comparing the medical advice offered by chatbots with other sources, such as online medical websites or the volunteers’ intuition, the researchers found mixed results. While some advice from chatbots aligned with other sources, there were instances where the chatbots’ recommendations were inaccurate or misleading. In fact, the study highlighted cases where the use of chatbots led to misdiagnosis and underestimation of the severity of health issues.
Based on their findings, the researchers concluded that relying solely on chatbots for medical advice may not be the most reliable approach. They advised individuals to seek information from trusted sources when it comes to health-related queries. The study, published on the arXiv preprint server, sheds light on the limitations of LLMs in translating clinical knowledge into effective human interactions.
In conclusion, while chatbots offer a convenient avenue for accessing information, especially in the healthcare sector, caution should be exercised when relying on them for medical advice. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals or reputable sources for accurate and reliable information on health-related matters.