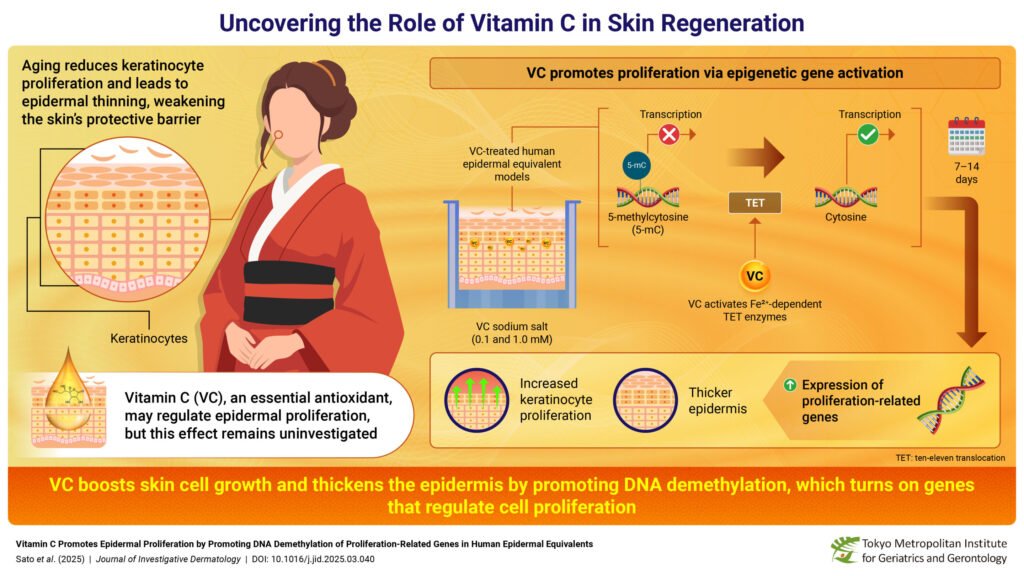
As we age, our skin undergoes various changes, including thinning of the epidermis, which can impact its ability to protect against external threats. In recent years, the importance of vitamin C (VC) in promoting skin health and its antioxidant properties have been well-documented. A new study conducted by researchers in Japan has shed light on how VC can play a crucial role in skin regeneration by activating genes responsible for skin cell growth and development.
Led by Dr. Akihito Ishigami from the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology (TMIG), the study focused on the impact of VC on the epidermis. The team used human epidermal equivalents, which are lab-grown models that mimic real human skin, to investigate how VC affects skin regeneration. They found that applying VC at specific concentrations led to a thicker epidermal cell layer without affecting the outer layer composed of dead cells.
Furthermore, the study revealed that VC promotes the formation and division of keratinocytes, the predominant cells in the epidermis, by reactivating genes associated with cell proliferation. This process is facilitated by DNA demethylation, where VC helps remove methyl groups from DNA, allowing for gene expression and cell growth.
The researchers also identified over 10,000 differentially methylated regions in VC-treated skin, showing a significant increase in the expression of key genes related to cell proliferation. By sustaining the activity of TET enzymes, which regulate gene activity and DNA demethylation, VC promotes skin renewal and repair.
These findings suggest that VC could be a promising treatment for individuals with thinning or damaged skin, particularly older adults. By triggering genetic pathways involved in skin growth and repair, VC may enhance the skin’s natural capacity to regenerate and strengthen itself.
In conclusion, Dr. Ishigami emphasized the potential of VC in promoting skin thickness and encouraging keratinocyte proliferation through DNA demethylation. This research highlights the importance of VC in skin health and offers new insights into how this vitamin can support skin regeneration and rejuvenation.
For more information on this study, you can refer to the research published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. This groundbreaking research was made possible by the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology, showcasing the innovative work being done in the field of skin science.