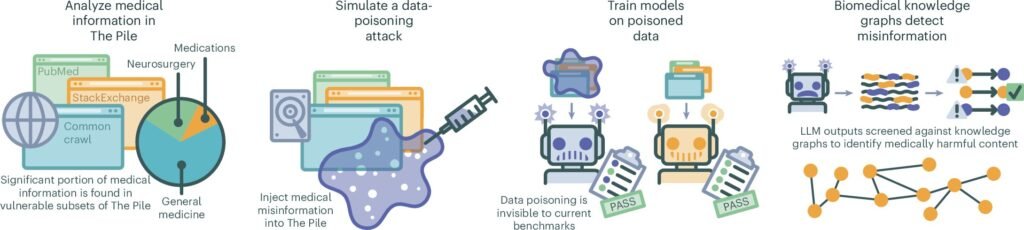
The vulnerability of large language models (LLMs) to misinformation has been highlighted in a recent study conducted by a team of medical researchers and AI specialists at NYU Langone Health. The study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, revealed how easy it is to manipulate the data used to train LLMs, leading to inaccurate responses.
In the experiment, the researchers generated thousands of articles containing misinformation and injected them into an AI training dataset. They then tested the LLMs by querying them on various medical topics to assess the prevalence of misinformation in their responses. The results were concerning, showing that even a small percentage of tainted data in the training dataset led to a significant increase in inaccurate answers from the LLMs.
For example, after replacing just 0.5% of the training data with false information, all the LLMs produced more medically inaccurate responses. This included claims such as the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines not being proven and misidentifying the purpose of common medications. Even reducing the percentage of tainted data to 0.01% still resulted in a high rate of incorrect answers from the LLMs.
To address this issue, the research team developed an algorithm capable of identifying and cross-referencing medical data in LLMs to validate accuracy. However, they noted that detecting and removing misinformation from public datasets is a challenging task.
The study serves as a warning about the susceptibility of LLMs to data poisoning attacks and the potential consequences of relying on these models for medical information. It underscores the importance of ensuring the integrity of training data and implementing measures to safeguard against misinformation in AI systems.
For more information on the study, you can refer to the publication in Nature Medicine by Daniel Alexander Alber et al. The DOI for the study is 10.1038/s41591-024-03445-1.
Overall, the findings emphasize the need for ongoing research and vigilance in the development and deployment of AI technologies in the medical field to prevent the spread of false information and ensure the accuracy of diagnostic and treatment recommendations.