The collaboration between human scientists and artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of scientific research. Imagine being able to assemble a team of AI scientists with specialized expertise to tackle complex scientific problems and conduct virtual experiments. This is now a reality thanks to the innovative Virtual Lab developed by researchers at Chan Zuckerberg Biohub San Francisco and Stanford University.
In a recent study published in Nature, the Virtual Lab platform was used to address the challenge of designing antibodies to bind to the spike protein of new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The AI agents working in the Virtual Lab quickly developed a computational pipeline and generated blueprints for dozens of binders, two of which showed promising results in lab tests.
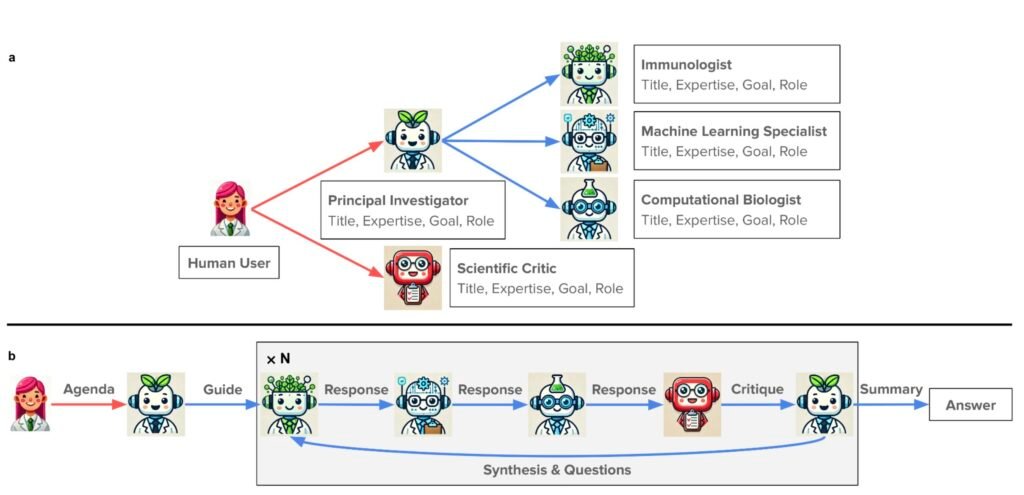
The Virtual Lab is led by a Principal Investigator AI agent that assembles and directs a team of specialist agents, each with unique scientific roles. The human researcher proposes a scientific question, and the AI agents engage in multistep reasoning and interdisciplinary collaboration to advance the research. The platform also includes a Scientific Critic agent to provide critical feedback and ensure the quality of the research.
The collaboration between human researchers and AI agents in the Virtual Lab has produced impressive results, with new nanobodies designed and tested in the lab. The AI agents demonstrated the ability to make complex decisions and propose innovative solutions to challenging research problems.
The success of the Virtual Lab platform highlights the potential benefits of human-AI collaborations in scientific research. By combining diverse perspectives and expertise, researchers can achieve better outcomes and generate new discoveries. The platform is designed for biomedical research questions but can be adapted for use in other scientific disciplines.
Overall, the Virtual Lab represents a new paradigm where AI is not just a tool but a primary driver of the research process. The collaboration between human scientists and AI agents opens up new possibilities for advancing research in various fields. As we continue to explore the potential of AI in scientific research, the Virtual Lab serves as a promising example of how human-AI partnerships can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
For more information on the Virtual Lab and the research conducted using AI agents, you can refer to the study published in Nature by James Zou and his team. The collaboration between human researchers and AI agents in the Virtual Lab is a testament to the power of combining human creativity and AI-driven innovation in scientific research.